Running Benchmarks
Benchmark experiments should be run with every functional change to the code. This is how you do it.
Whenever you change something in the code's functionality, you need to run the benchmark experiments to ensure it doesn't impede performance and to verify end-to-end functionality. Also, if you implement an alternative approach, the benchmark experiments can be a good way to compare it to our current best implementation.
The benchmark test suite is designed to evaluate the performance of Monty in different scenarios. These include rotated and translated objects, noisy observations, similar objects, different action spaces, multiple LMs, multiple objects, real-world data, and continual unsupervised learning.
For more details on the current benchmark experiments, see this page.
When merging a change that impacts the performance on the benchmark experiments, you need to update the table in our documentation here.
How to Run a Benchmark Experiment
To run a benchmark experiment, simply call
python run.py experiment=run_name
and replace run_name with the name of the benchmark experiment. All benchmark experiment configs are in the src/tbp/monty/conf/experiment/ folder. So for example, for running the quickest benchmark experiment you would call
python run.py experiment=randrot_10distinctobj_surf_agent
Go Ahead and Run the Command Above!
If you run the
randrot_10distinctobj_surf_agentexperiment using the command above, you will be able to follow along with all the following data analysis guides since we use this as an example.This should take about 1.5 minutes on an M3 MacBook or 5 minutes distributed on 16 CPU cores.
How to Report Benchmark Performance
Within the Thousand Brains Project, we run benchmarks on standardized infrastructure and the data from these runs are posted in our documentation. You won't have access to this infrastructure, however, you can still use benchmarks as end-to-end tests before and after your changes.
To verify end-to-end functionality, you can run a sample of the benchmarks on your local machine using the code as it was prior to your changes. Then, after you make code changes, you can run the same sample of the benchmarks on your local machine using the code with your changes included. The benchmarks are deterministic, so the before and after benchmark runs will match if your changes had no effect (with some variation in timing). Similarly, the before and after benchmark runs will not match if your changes impact Monty performance. In both cases, it is helpful to provide your before and after benchmark data as part of the description in your Pull Request.
Where to Find the Results
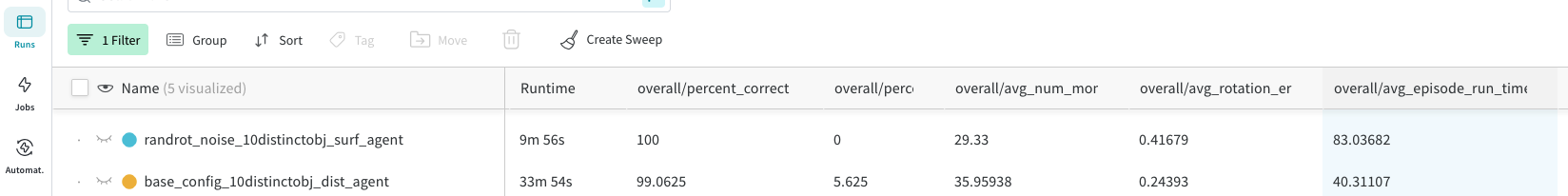
If you are using a wandb logger (used by default in the benchmark experiment configs), you can view the experiment results in the wandb dashboard. If you go into the "Runs" tab (selected on the left), you should see the summary statistics in the columns starting with "overall/".
If you are not using wandb, you can also calculate the statistics from the saved .csv file.
from tbp.monty.frameworks.utils.logging_utils import (load_stats,
print_overall_stats,
print_unsupervised_stats)
_, eval_stats, _, _ = load_stats(log_path + 'run_name',
load_train=False,
load_eval=True,
load_models=False,
load_detailed=False)
print_overall_stats(eval_stats)
# for the learning from scratch experiments, load the training csv instead and call
print_unsupervised_stats(train_stats, epoch_len=10) # 10 is the number of objects shown in an epoch
Where to Report the Results
If your benchmarks ran on the standardized infrastructure, and your code affected any of the benchmark results, you should update the benchmark results table here in the same PR. See our guide on contributing to documentation for instructions on how to edit documentation.
If your benchmarks ran on your local machine, please include the before and after data as part of the Pull Request description.
Help Us Make This Page Better
All our docs are open-source. If something is wrong or unclear, submit a PR to fix it!
Updated about 1 month ago
