Customizing Monty
For more info on contributing custom modules, see Ways to Contribute to Code
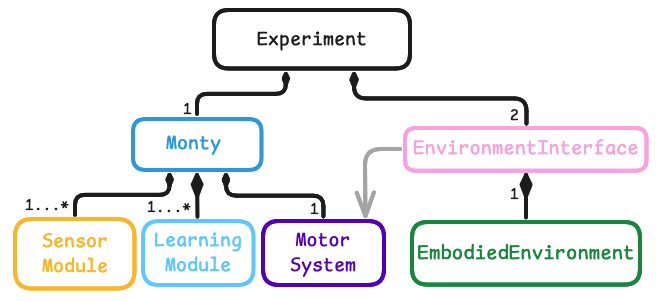
Monty is designed as a modular framework where a user can easily swap out different implementations of the basic Monty components. For instance you should be able to switch out the type of learning module used without changing the sensor modules, environment, or motor system. The basic components of Monty are defined as abstract classes abstract_monty_classes.py. To implement your own custom version of one of these classes, simply subclass from the abstract class or one of its existing subclasses.
Customizing a Class - Example: Learning Module
Here are step by step instructions of how to customize a LearningModule class as an example.
Learning modules (LMs) can be loosely compared to cortical columns, and each learning module receives a subset of the input features. At each time step, each learning module performs a modeling step and a voting step. In the modeling step, LMs update in response to sensory inputs. In the voting step, each LM updates in response to the state of other LMs. Note that the operations each LM performs during the step and receive_votes invocations are customizable.
There is a 3-step process for creating a custom learning module. All other classes can be customized along the same lines.
- Define a new subclass of LearningModule (LM) either in a local projects folder, or in
/src/tbp/monty/frameworks/models. See the abstract class definitions in/src/tbp/monty/frameworks/models/abstract_monty_classes.pyfor the functions that every LM should implement. - Define a config for your learning module. You are encouraged but not required to provide default arguments to your LM. It may also be helpful to specify some common configurations for your LM in
src/tbp/monty/conf/experiment/config/monty/learning_modules/learning_moduledirectory for use in your experiment configurations. Additionally, you could specify common expected configurations of multiple learning modules insrc/tbp/monty/conf/experiment/config/monty/learning_modulesby defining a dictionary of LM IDs and specifyinglearning_module_classand itslearning_module_argsfor each learning module. - Define an experiment config in
src/tbp/monty/conf/experiment/(or in your own repository or in yourmonty_labprojects folder).
You custom experiment config could look like this:
defaults:
- base_config_10distinctobj_dist_agent
- config/monty/clear_monty_config@config
- config/monty/[email protected]_config
- config/monty/learning_modules/[email protected]_config
config:
monty_config:
learning_module_configs:
learning_module_0:
learning_module_class: ${monty.class:path.to.your.CustomLM}
learning_module_args:
your_arg1: val1
your_arg2: val2
For simplicity we inherit all other default values from the base_config_10distinctobj_dist_agent config in src/tbp/monty/conf/experiment/base_config_10distinctobj_dist_agent.yaml and use the monty_config specified in src/tbp/monty/conf/experiment/config/monty/patch_and_view_sota.yaml.
Help Us Make This Page Better
All our docs are open-source. If something is wrong or unclear, submit a PR to fix it!
Updated 26 days ago
